United Arab Emirates
Discover the United Arab Emirates: Abu Dhabi & Dubai highlights, food, culture, top attractions, travel tips and practical visitor info.
About Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia, the heart of the Islamic world, is known for its spiritual significance, rich history, desert landscapes, and modern economic growth.
Quick Facts

Quick Facts — Saudi Arabia
• Official name: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
• Capital: Riyadh
• Largest city: Riyadh
• Population: ~35,841,000 (2025 est.)
• Area: ~2,149,690 km²
• Currency: Saudi Riyal (SAR)
• Official language: Arabic
• Time zone: UTC+3 (Arabia Standard Time)
• Calling code: +966
• Internet TLD: .sa
• ISO code: SA / SAU
Food & Cuisine
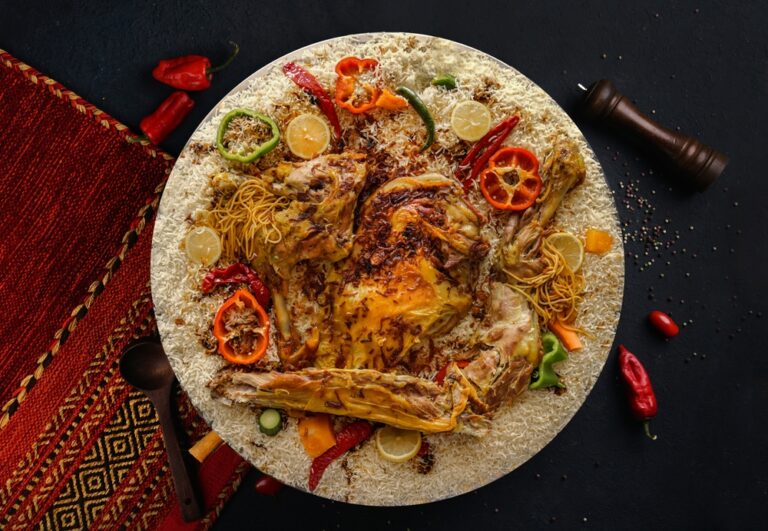
Saudi cuisine reflects the country’s Bedouin heritage and Islamic influences. Staple foods include rice, lamb, chicken, dates, and bread. Popular dishes include Kabsa (spiced rice with meat), Jareesh (crushed wheat porridge), and Mandi (slow-cooked rice and meat). Arabic coffee and dates remain symbols of hospitality, while modern Saudi cities also embrace a wide variety of international cuisines.





RELIGION & BELIEFS
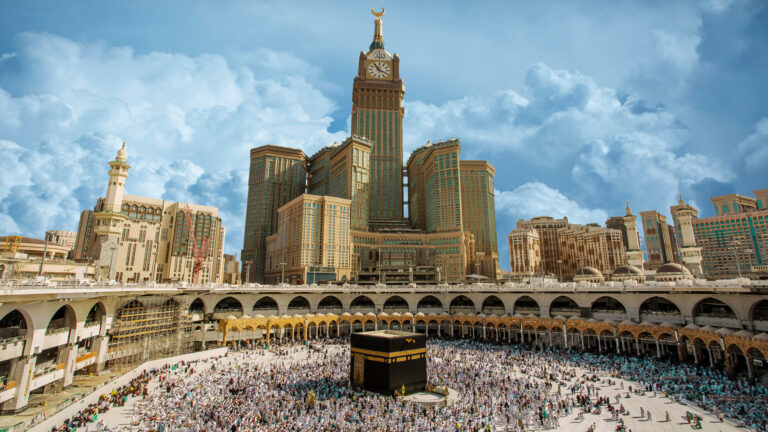
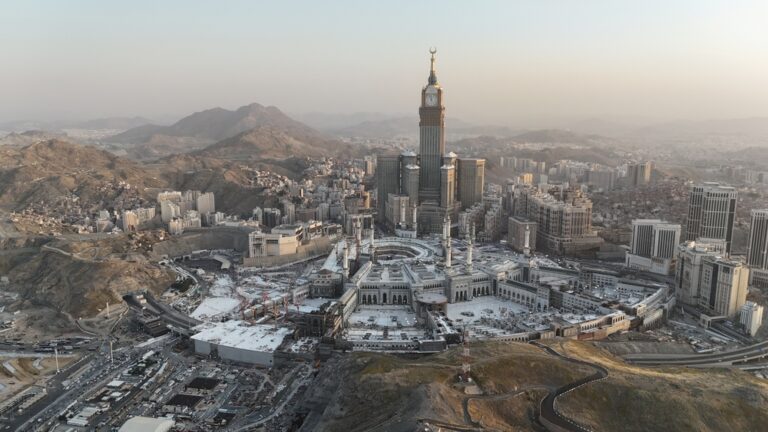
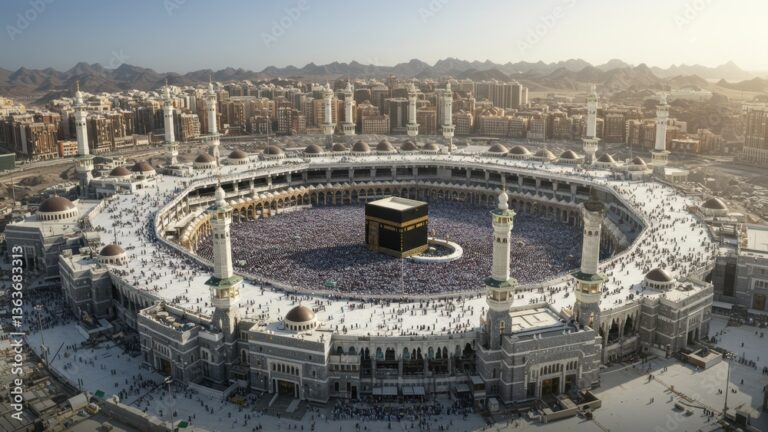
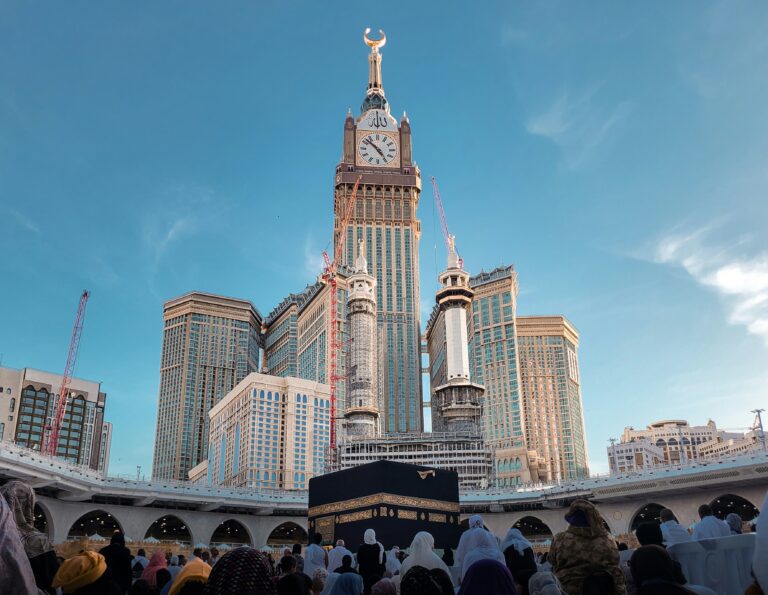
As the birthplace of Islam, Saudi Arabia holds immense religious significance. It is home to the holy cities of Mecca and Medina, which attract millions of Muslims annually for Hajj and Umrah. Islam shapes all aspects of life, from daily prayer routines to social norms and national holidays. The majority of Saudis follow Sunni Islam, and religious values are deeply interwoven with the kingdom’s culture, governance, and global influence as the spiritual heart of the Muslim world.




Language
The official language of Saudi Arabia is Arabic, with Modern Standard Arabic used in formal contexts. In everyday life, regional dialects such as Najdi, Hejazi, and Gulf Arabic are common. English is also widely spoken in business, education, and urban areas, making communication easier for international visitors.


Traditions
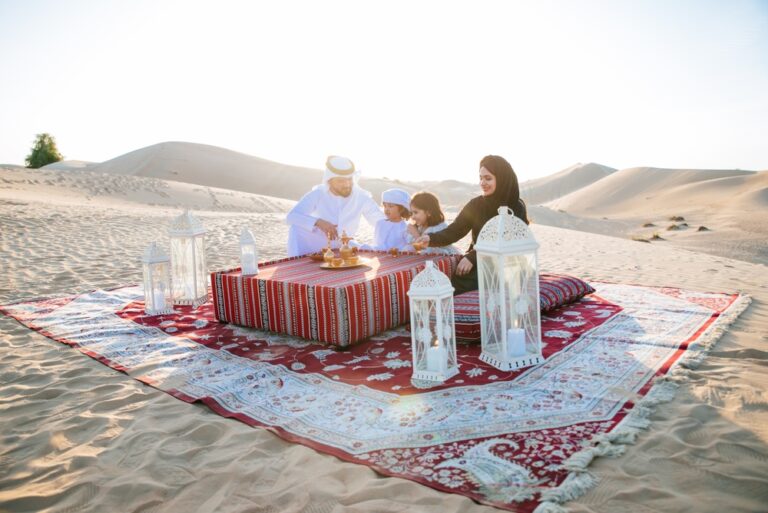
Traditional Saudi customs highlight modesty, respect, and generosity. Men commonly wear the thobe (a long white robe) with a ghutra (headscarf), while women traditionally wear the abaya (a long black cloak). Family ties are strong, and social gatherings play an important role in community life. Major traditions include celebrating Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha with prayer, feasting, and large family gatherings.

Famous Places
Saudi Arabia is home to some of the world’s most renowned landmarks. Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam, attract millions of pilgrims every year. Modern marvels such as Riyadh’s Kingdom Centre Tower symbolize progress, while heritage sites like Diriyah and the ancient rock formations of Al-Ula showcase the nation’s history. Along the Red Sea coast, new luxury destinations are emerging, making Saudi Arabia a blend of spiritual, cultural, and modern attractions.

Attire
Traditional clothing in Saudi Arabia reflects cultural identity and modesty. Men typically wear the thobe, a long white robe, along with the ghutra or shemagh, a headscarf held by an agal. Women traditionally wear the abaya, a long black cloak, with some also choosing the niqab or hijab. In recent years, modern styles and colors have emerged, especially among the younger generation, blending tradition with contemporary fashion while maintaining cultural values.

Lifestyle
Life in Saudi Arabia combines traditional values with rapid modernization. Family remains central, with gatherings and hospitality forming the heart of daily life. In cities, young people enjoy shopping malls, cafés, cinemas, and sporting events, reflecting global influences. At the same time, rural communities maintain a slower pace, rooted in heritage and close-knit ties. This blend creates a lifestyle where tradition and innovation coexist, shaping a dynamic national identity.

National Symbols
Saudi Arabia’s national symbols embody faith, unity, and heritage. The green flag bears the Islamic declaration of faith and a sword symbolizing justice. The national emblem features two crossed swords with a palm tree, representing prosperity and strength. The Arabian camel and falcon are cultural icons tied to Bedouin history, while September 23, Saudi National Day, marks the unification of the kingdom, celebrated nationwide with pride and festivity.

Population
In 2025, Saudi Arabia’s population is estimated at about 36 million, with a youthful demographic — more than 60% are under the age of 35. This young generation plays a vital role in shaping the nation’s future, driving cultural change, education, and workforce development. Alongside citizens, a diverse expatriate community from South Asia, Africa, and Western countries contributes significantly to the economy, creating a multicultural society within the kingdom.

Infrastructure
Saudi Arabia is undergoing massive infrastructure transformation under Vision 2030. Projects like the futuristic NEOM smart city, the Riyadh Metro, and large-scale airport expansions are redefining urban living and transportation. The Red Sea tourism projects highlight sustainability and luxury, attracting global attention. These investments not only modernize daily life for citizens but also position Saudi Arabia as a hub for innovation, tourism, and international connectivity in the region.

GDP & Economy
Saudi Arabia’s economy is among the largest in the Middle East, with a 2025 GDP estimated at $1.1 trillion. Oil remains central, with the kingdom being the world’s top exporter through Saudi Aramco, yet the nation is rapidly diversifying. Tourism, technology, logistics, and finance are becoming new pillars of growth under Vision 2030, reducing reliance on oil and opening doors to global investment and partnerships.

Government
Saudi Arabia is an absolute monarchy, ruled by the Al Saud family. The King serves as head of state, while the Crown Prince currently drives reform initiatives under Vision 2030. Governance is deeply tied to Islamic law, ensuring that religion remains central to decision-making. At the same time, the government is introducing modernization policies, from women’s empowerment to economic diversification, balancing tradition with future-focused reforms.

Social Factors
Saudi society values hospitality, generosity, and family unity. Traditional roles are evolving, with women increasingly participating in education, sports, and the workforce. Social reforms have expanded entertainment options, from cinemas to concerts, changing daily life. Despite modernization, the kingdom maintains strong communal ties, where respect for elders, cultural etiquette, and collective identity continue to define social interactions.

Education System
Education in Saudi Arabia has expanded rapidly, with a strong emphasis on both religious studies and modern sciences. The government invests heavily in schools and universities, with institutions like King Saud University and KAUST recognized globally. New programs focus on STEM, technology, and research, preparing the youth for future industries. Scholarships abroad and educational reforms under Vision 2030 are shaping a generation ready for international collaboration.

Social Inclusion & Unity
National initiatives emphasize unity across tribes, genders, and regions, promoting equal opportunities and inclusion. Women are increasingly taking leadership roles, while youth-driven movements encourage innovation and entrepreneurship. Events like Saudi National Day and sporting celebrations foster patriotism and collective identity. These efforts strengthen the kingdom’s social fabric, ensuring diversity and inclusion are part of its long-term growth.

Environment
Saudi Arabia’s vast deserts, mountain ranges, and Red Sea coastline create a unique natural environment. To address climate challenges, the government launched the Saudi Green Initiative, focusing on renewable energy, reforestation, and reducing carbon emissions. Eco-tourism projects along the Red Sea highlight a growing balance between environmental preservation and development, showcasing the kingdom’s commitment to sustainable living for future generations.

Technology
Technology plays a central role in Saudi Arabia’s transformation. Investments in artificial intelligence, fintech, and renewable energy are creating a digital economy. Projects like NEOM aim to be hubs of smart living with advanced infrastructure. Widespread adoption of e-governance, 5G connectivity, and digital banking reflects the country’s ambition to lead in technological innovation across the region and beyond.





International Relations
Saudi Arabia holds a key position on the global stage as a G20 member and a leading voice in OPEC. It maintains strong ties with the United States, China, and neighboring Arab nations, balancing diplomacy with strategic partnerships. Its role in the Muslim world gives it significant influence, while ongoing regional and global cooperation ensures the kingdom remains central to international politics and trade.
